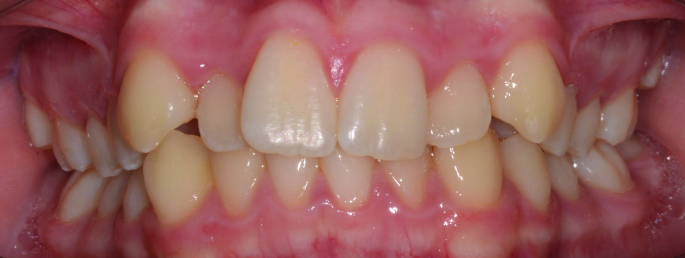
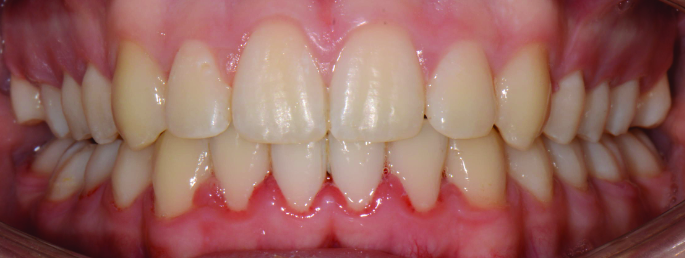
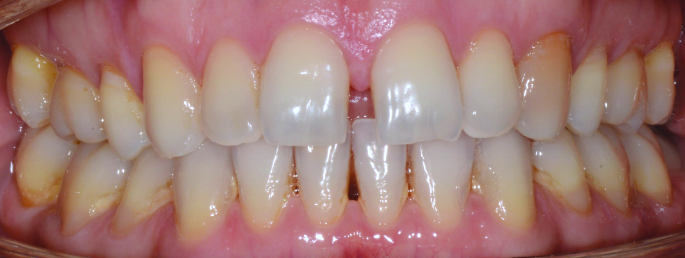
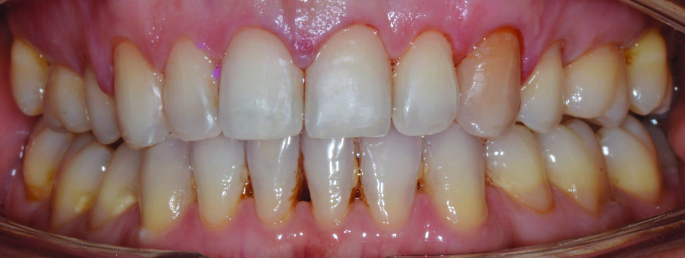
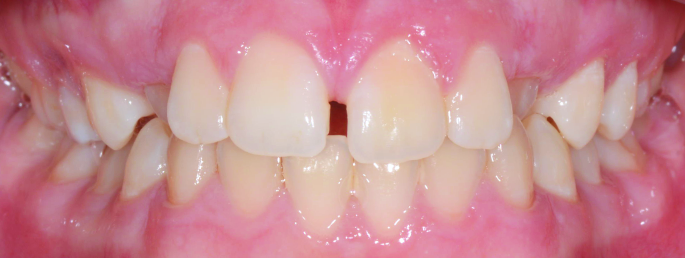
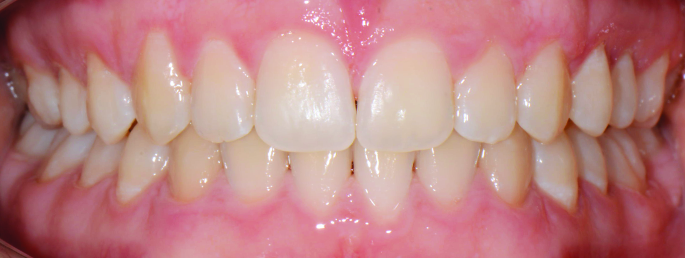
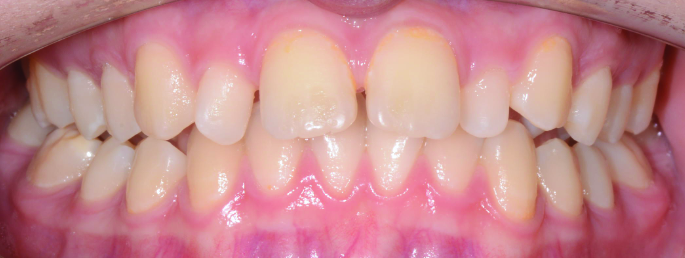
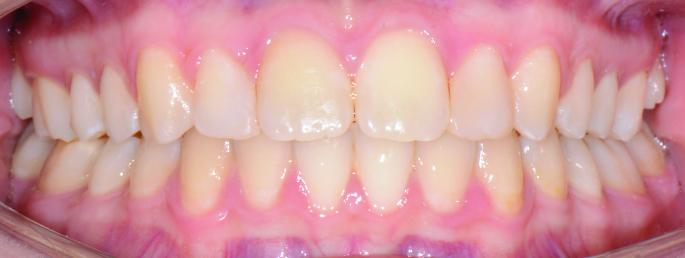
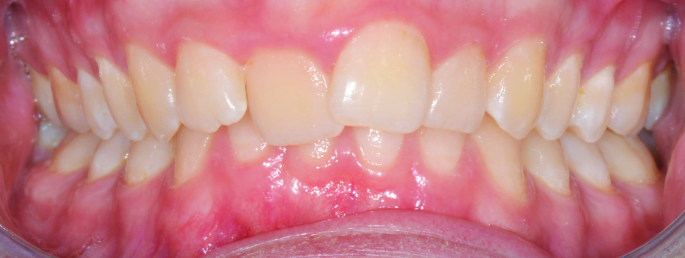
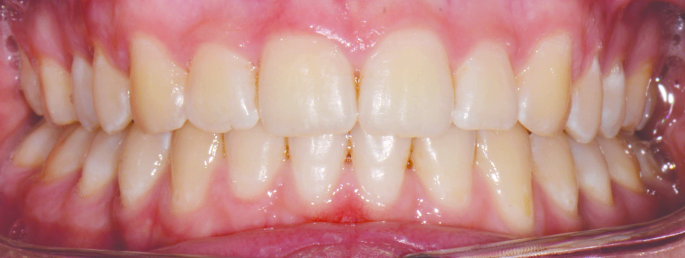
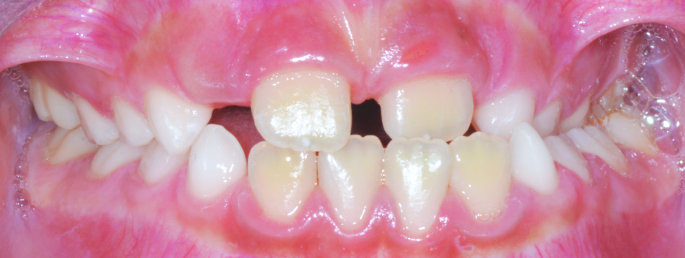
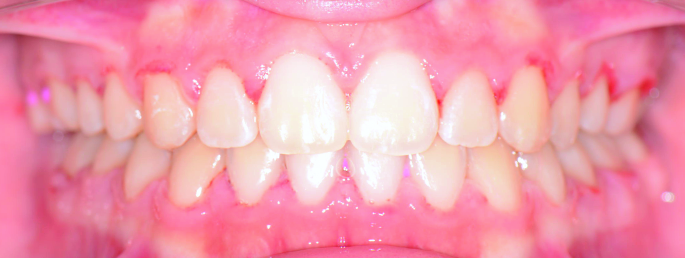
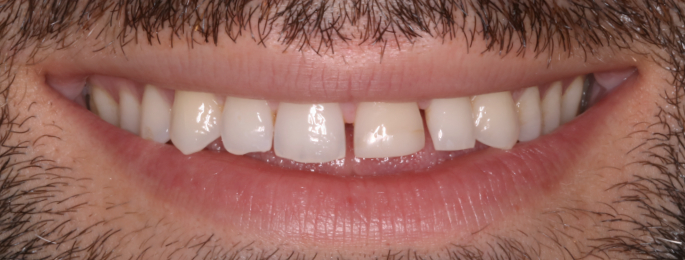
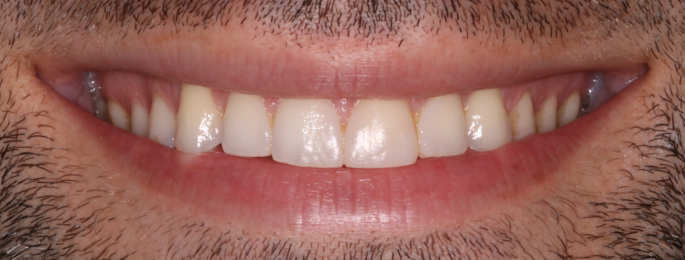
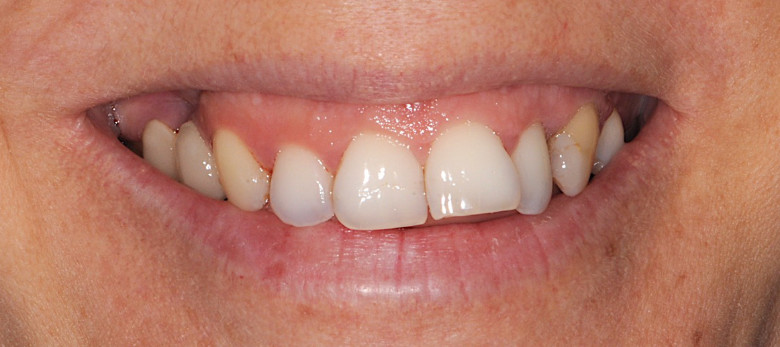
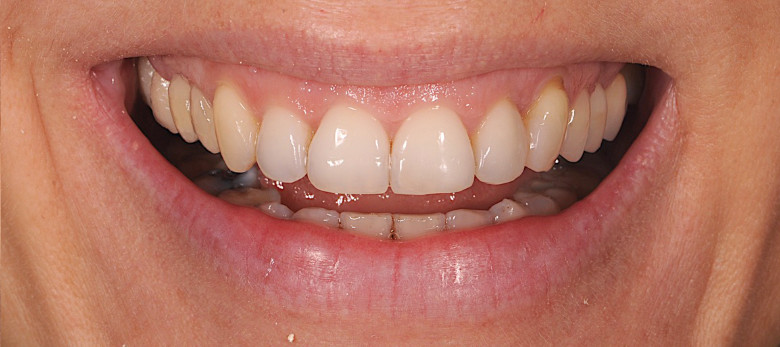
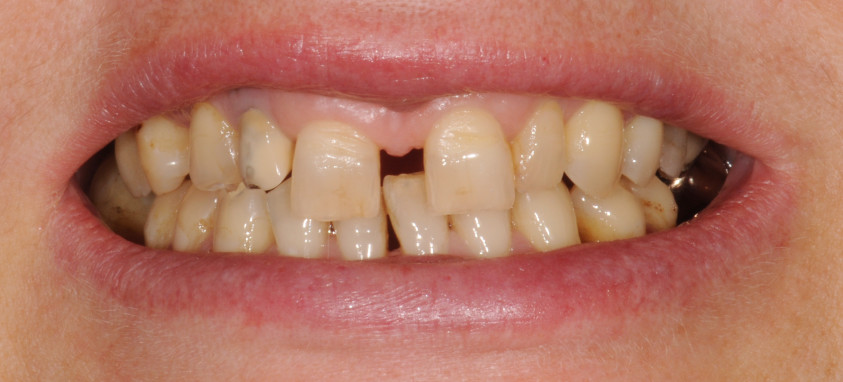
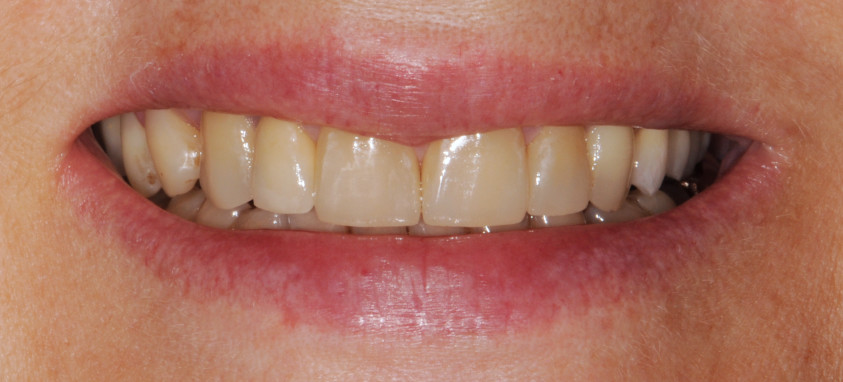
Orthodontics is the specialized branch of Dentistry that deals with the correction of dentofacial structures (teeth and jaw bones) both during growth (childhood orthodontics) and in maturity (adult orthodontics). In practice, Orthodontics deals with the Diagnosis, Prevention, Interception and Treatment of incorrect dental occlusions, through the most suitable intervention for achieving and subsequently maintaining correct relationships between teeth and good harmony and aesthetics.
Orthodontic treatment often involves an intervention on skeletal growth, therefore the orthodontist must have a good knowledge not only of dental development, but also of craniofacial growth. The presence of irregular or incorrectly occluded teeth can cause: functional problems (including difficulty in mandibular movements with pain and muscle incoordination and temporomandibular joint disorders), problems with chewing, swallowing and phonation, greater susceptibility to dental trauma and periodontal problems, psychosocial problems (related to facial aesthetics and poor acceptance).
Orthodontics is divided into:
- Dentofacial orthopedics whose objective is to resolve bone growth imbalances before this condition becomes structured in such a way as to require a combined orthodontic-surgical approach
- Fixed orthodontics which aims to correct dental malpositions in order to achieve the functional and aesthetic recovery of the permanent dentition.
Discover the cases
Potrebbe interessarti anche…
L'ortodonzia invisibile rappresenta una delle innovazioni più significative nel campo dell'odontoiatria moderna. Contrariamente ai tradizionali apparecchi metallici, ...
Il riallineamento dei denti storti o affollati è una pratica odontoiatrica fondamentale per migliorare la salute orale ...
I denti storti possono avere conseguenze sulla salute orale e generale come ad esempio: Difficoltà nella pulizia: I ...